In this Personal View, we discuss current knowledge on SARS-CoV-2 RNA or antigen persistence in children infected with SARS-CoV-2. Based on the evidence that the virus can persist in adults, we have done a literature review and analysed studies that looked for SARS-CoV-2 RNA or antigens in children undergoing autopsy, biopsy, or surgery for either death from COVID-19 or multisystem inflammatory syndrome, or assessments for long COVID-19 or other conditions. Our analysis suggests that in children, independent from disease severity, SARS-CoV-2 can spread systemically and persist for weeks to months. We discuss what is known about the biological effects of viral persistence for other viral infections and highlight new scenarios for clinical, pharmacological, and basic research exploration. Such an approach will improve the understanding and management of post-viral syndromes.
Viral persistence in children infected with SARS-CoV-2: current evidence and future research strategies
Jun 26, 2023|The Lancet Microbe
Related Content
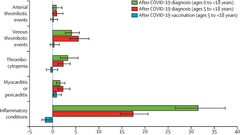
Vascular and inflammatory diseases after COVID-19 infection and vaccination in children and young people in England: a retrospective, population-based cohort study using linked electronic health records
ABSTRACT Background The rarity of severe diseases following COVID-19 infection balanced against...

Long COVID associated with SARS-CoV-2 reinfection among children and adolescents in the omicron era (RECOVER-EHR): a retrospective cohort study
Background Post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC) remain a major public health chall...

Characteristics and predictors of Long Covid in children: a 3-year prospective cohort study
Background Children can develop Long Covid, however long term outcomes and their predictors are ...
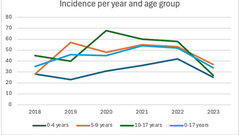
Increased Incidence of Type 1 Diabetes and Co-Existing Thyroid Autoimmunity During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Sweden
ABSTRACT Aim We aimed to investigate if the incidence of type 1 diabetes increased in children ...
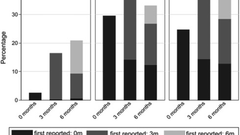
Long COVID in Children and Young after Infection or Reinfection with the Omicron Variant: A Prospective Observational Study
ABSTRACT To describe the prevalence of long COVID in children infected for the first time (n = 3...