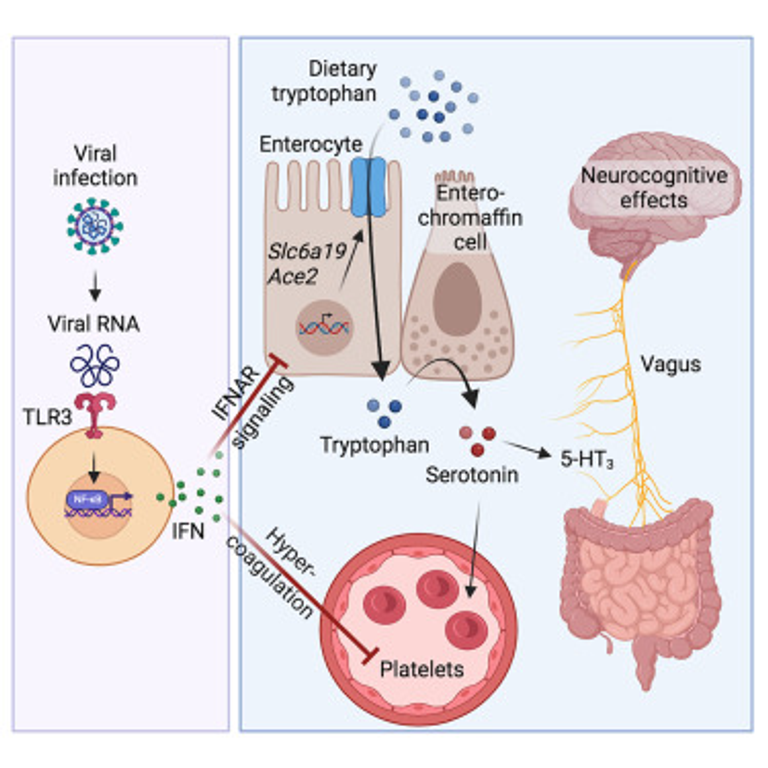
Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC, “Long COVID”) pose a significant global health challenge. The pathophysiology is unknown, and no effective treatments have been found to date. Several hypotheses have been formulated to explain the etiology of PASC, including viral persistence, chronic inflammation, hypercoagulability, and autonomic dysfunction. Here, we propose a mechanism that links all four hypotheses in a single pathway and provides actionable insights for therapeutic interventions. We find that PASC are associated with serotonin reduction. Viral infection and type I interferon-driven inflammation reduce serotonin through three mechanisms: diminished intestinal absorption of the serotonin precursor tryptophan; platelet hyperactivation and thrombocytopenia, which impacts serotonin storage; and enhanced MAO-mediated serotonin turnover. Peripheral serotonin reduction, in turn, impedes the activity of the vagus nerve and thereby impairs hippocampal responses and memory. These findings provide a possible explanation for neurocognitive symptoms associated with viral persistence in Long COVID, which may extend to other post-viral syndromes.
Serotonin reduction in post-acute sequelae of viral infection
Oct 16, 2023|Cell
Related Content
Immunological dysfunction persists for 8 months following initial mild-to-moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection
ABTRACT A proportion of patients surviving acute coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection d...

Postacute sequelae of COVID-19 at 2 years
Abstract Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection can lead to post...
SARS-CoV-2 reservoir in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC)
ABSTRACT Millions of people are suffering from Long COVID or post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PA...

Long-COVID-19 autonomic dysfunction: An integrated view in the framework of inflammaging
ABSTRACT: The recently identified syndrome known as Long COVID (LC) is characterized by a conste...
Long COVID: major findings, mechanisms and recommendations
ABSTRACT Long COVID is an often debilitating illness that occurs in at least 10% of severe acute...