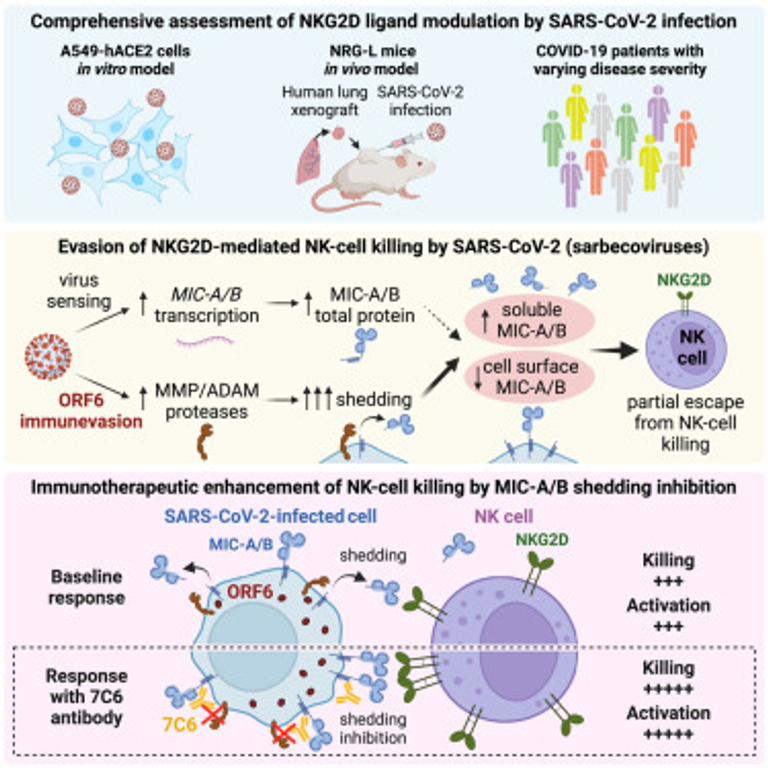
SARS-CoV-2 and other sarbecoviruses continue to threaten humanity, highlighting the need to characterize common mechanisms of viral immune evasion for pandemic preparedness. Cytotoxic lymphocytes are vital for antiviral immunity and express NKG2D, an activating receptor conserved among mammals that recognizes infection-induced stress ligands (e.g., MIC-A/B). We found that SARS-CoV-2 evades NKG2D recognition by surface downregulation of MIC-A/B via shedding, observed in human lung tissue and COVID-19 patient serum. Systematic testing of SARS-CoV-2 proteins revealed that ORF6, an accessory protein uniquely conserved among sarbecoviruses, was responsible for MIC-A/B downregulation via shedding. Further investigation demonstrated that natural killer (NK) cells efficiently killed SARS-CoV-2-infected cells and limited viral spread. However, inhibition of MIC-A/B shedding with a monoclonal antibody, 7C6, further enhanced NK-cell activity toward SARS-CoV-2-infected cells. Our findings unveil a strategy employed by SARS-CoV-2 to evade cytotoxic immunity, identify the culprit immunevasin shared among sarbecoviruses, and suggest a potential novel antiviral immunotherapy.
Evasion of NKG2D-mediated cytotoxic immunity by sarbecoviruses
Apr 22, 2024|Cell
Premium
COVID-19 & the Immune System
Related Content
Severe COVID-19 induces prolonged elevation of the acute-phase protein pentraxin 3
ABSTRACT Introduction: During the acute-phase of COVID-19, elevated levels of several acute-phas...

Differential decline of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody levels, innate and adaptive immune cells, and shift of Th1/inflammatory to Th2 serum cytokine levels long after first COVID-19
ABSTRACT Background SARS-CoV-2 has triggered a pandemic and contributes to long-lasting morbidi...
Molecular mimicry in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children
ABSTRACT Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) is a severe, post-infectious sequ...

SARS-CoV-2 S1 subunit produces a protracted priming of the neuroinflammatory, physiological, and behavioral responses to a remote immune challenge: A role for corticosteroids
ABSTRACT Long COVID is a major public health consequence of COVID-19 and is characterized by mul...

Differential decline of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody levels, innate and adaptive immune cells, and shift of Th1/inflammatory to Th2 serum cytokine levels long after first COVID-19
ABSTRACT Background SARS-CoV-2 has triggered a pandemic and contributes to long-lasting morbidi...